Uttar Pradesh State
Critical minerals, policy, and the energy transition
The Energy Transition in Uttar Pradesh, India
Uttar Pradesh, India’s most populous state s,tretching from the Himalayan foothills to the Vindhyan plateau, is overhauling a coal-centred grid to meet surging power demand that topped 28 GW in the May 2025 heatwave. Installed capacity is about 29 GW: roughly 19 GW coal-gas, 2.8 GW solar, 1.6 GW biomass-bagasse and small hydro, plus imports from the northern grid. The Uttar Pradesh Solar Energy Policy 2022 targets 22 GW solar, 5 GW wind–solar hybrids and 2 GWh batteries by 2030. Flagship schemes include the 4 GW Bundelkhand Ultra-Mega Renewable Park, 1 GW of canal-top PV along the Upper Ganga network, and a 600 MW floating array on the Rihand reservoir. A 1,000 MWh battery hub planned near Prayagraj will shift midday surplus into evening household peaks, while Mathura refinery is installing a 20 MW electrolyser for green hydrogen blending in transport fuels. Rooftop programmes aim for 1 GW across 200,000 schools, warehouses and government buildings. The state’s critical mineral base complements its clean-energy ambitions and industrial expansion. Sonbhadra hosts copper, gold and silica belts; Banda carries bauxite and diaspore for aluminium and ceramics, while potash-bearing alluvium near Kanpur is earmarked for domestic fertiliser feedstock. By pairing gigawatt-scale solar, large-volume storage and this diverse resource base, Uttar Pradesh is positioning itself as a northern hub for low-carbon power and advanced materials.
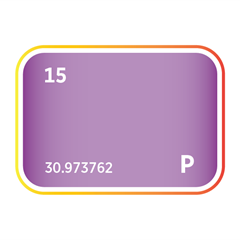
Critical Minerals produced in Uttar Pradesh
Energy Raw Materials and products produced in Uttar Pradesh
Essential Mineral Production and Products in Uttar Pradesh
A state-by-state analysis of India’s critical minerals and energy transition policies
SFA explores the state-level frontlines of India’s strategy to secure its position in the global energy transition. As demand surges for critical minerals used in electric vehicles, grid storage, solar, and hydrogen technologies, India is intensifying efforts to diversify supply, localise processing, and reduce strategic dependencies. This analysis examines how mineral endowments, state-level industrial policy, and renewable energy deployment intersect across the Indian landscape. From lithium-bearing pegmatites in Karnataka and Jammu & Kashmir to rare-earth-rich coastal sands in Tamil Nadu and Odisha, this state-by-state review highlights the opportunities and constraints shaping India’s clean-energy future and its role in global mineral security.

Meet the Critical Minerals team
Trusted advice from a dedicated team of experts.

Henk de Hoop
Chief Executive Officer

Beresford Clarke
Managing Director: Technical & Research

Jamie Underwood
Principal Consultant

Dr Jenny Watts
Critical Minerals Technologies Expert

Ismet Soyocak
ESG & Critical Minerals Lead

Thomas Shann Mills
Senior Machine Learning Engineer

Rj Coetzee
Senior Market Analyst: Battery Materials and Technologies

Franklin Avery
Commodity Analyst

Shunjie Zhao (Tony)
Commodity Analyst: APAC

How can we help you?
SFA (Oxford) provides bespoke, independent intelligence on the strategic metal markets, specifically tailored to your needs. To find out more about what we can offer you, please contact us.