Madhya Pradesh State
Critical minerals, policy, and the energy transition
The Energy Transition in Madhya Pradesh, India
Madhya Pradesh, sprawling across the Narmada valley and Vindhyan plateau, is building a central‐Indian clean-power backbone. Installed capacity tops 32 GW, with coal still dominant but more than 9 GW of renewables already in service: 5.4 GW solar, 2 GW hydro and 1.8 GW wind. Flagship projects include the 750 MW Rewa Solar Park, 1,500 MW of new arrays at Agar, Shajapur and Neemuch, and 600 MW of canal-top PV on the Narmada irrigation network. The state’s Renewable Energy Policy targets 20 GW solar and 3 GW wind–solar hybrids by 2030, backed by a 1 GWh pumped-storage upgrade at Gandhi Sagar and a 700 MWh battery hub near Indore to shift midday surplus into the evening peak. A green-hydrogen pilot at Jabalpur ordnance factory will tap round-the-clock solar from Rewa. The state’s crust is equally strategic. The Malanjkhand complex hosts India’s largest copper deposit with associated molybdenum and cobalt, while Panna’s kimberlite pipes supply diamonds for electronics and cutting tools. Manganese belts in Balaghat, graphite showings in Betul and potash brines in Satna expand the critical-mineral basket. By coupling gigawatt-scale solar and storage with this diverse resource base, Madhya Pradesh is positioning itself as a heartland hub for low-carbon power and advanced materials.
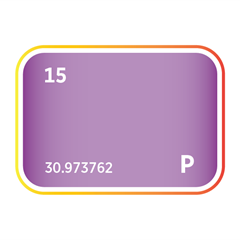
Critical Minerals produced in Madhya Pradesh
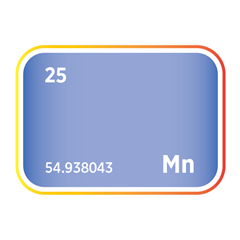
Energy Raw Materials and products produced in Madhya Pradesh
Essential Mineral Production and Products in Madhya Pradesh
A state-by-state analysis of India’s critical minerals and energy transition policies
SFA explores the state-level frontlines of India’s strategy to secure its position in the global energy transition. As demand surges for critical minerals used in electric vehicles, grid storage, solar, and hydrogen technologies, India is intensifying efforts to diversify supply, localise processing, and reduce strategic dependencies. This analysis examines how mineral endowments, state-level industrial policy, and renewable energy deployment intersect across the Indian landscape. From lithium-bearing pegmatites in Karnataka and Jammu & Kashmir to rare-earth-rich coastal sands in Tamil Nadu and Odisha, this state-by-state review highlights the opportunities and constraints shaping India’s clean-energy future and its role in global mineral security.

Meet the Critical Minerals team
Trusted advice from a dedicated team of experts.

Henk de Hoop
Chief Executive Officer

Beresford Clarke
Managing Director: Technical & Research

Jamie Underwood
Principal Consultant

Dr Jenny Watts
Critical Minerals Technologies Expert

Ismet Soyocak
ESG & Critical Minerals Lead

Thomas Shann Mills
Senior Machine Learning Engineer

Rj Coetzee
Senior Market Analyst: Battery Materials and Technologies

Franklin Avery
Commodity Analyst

Shunjie Zhao (Tony)
Commodity Analyst: APAC

How can we help you?
SFA (Oxford) provides bespoke, independent intelligence on the strategic metal markets, specifically tailored to your needs. To find out more about what we can offer you, please contact us.